Recently, I have seen lots of mommy asking about probiotic supplements? Many health benefits about probiotics have been advertised, but it is often hard to know what is true? Does your child need probiotic supplements? Before you learn about probiotics, have you heard about prebiotics? What are their health benefits? Read on to learn the difference between prebiotics and probiotics and their health benefits.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PREBIOTICS AND PROBIOTICS?
Prebiotics are non-digestible carbohydrates that act as “food” for probiotics. Eating prebiotics will help probiotics grow and remain in our digestive system.
Probiotics are healthy/good bacteria that naturally live in the colon of our digestive systems. Probiotics help to keep a balance between the good and bad bacteria that live in your colon. Certain probiotics have been linked to specific health benefits.
TYPE OF PREBIOTICS
The most common prebiotics include:
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) or fructans
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Inulin (a types of FOS)
PREBIOTICS IN NATURAL FOODS
Inulin
Due to the pleasant taste characteristics and low-calorie status, FOS and inulin have been added to many food products. Inulin has a creamy, catlike texture that makes it a good fat substitute. You will find it in many spreads, salad dressings, dairy products.
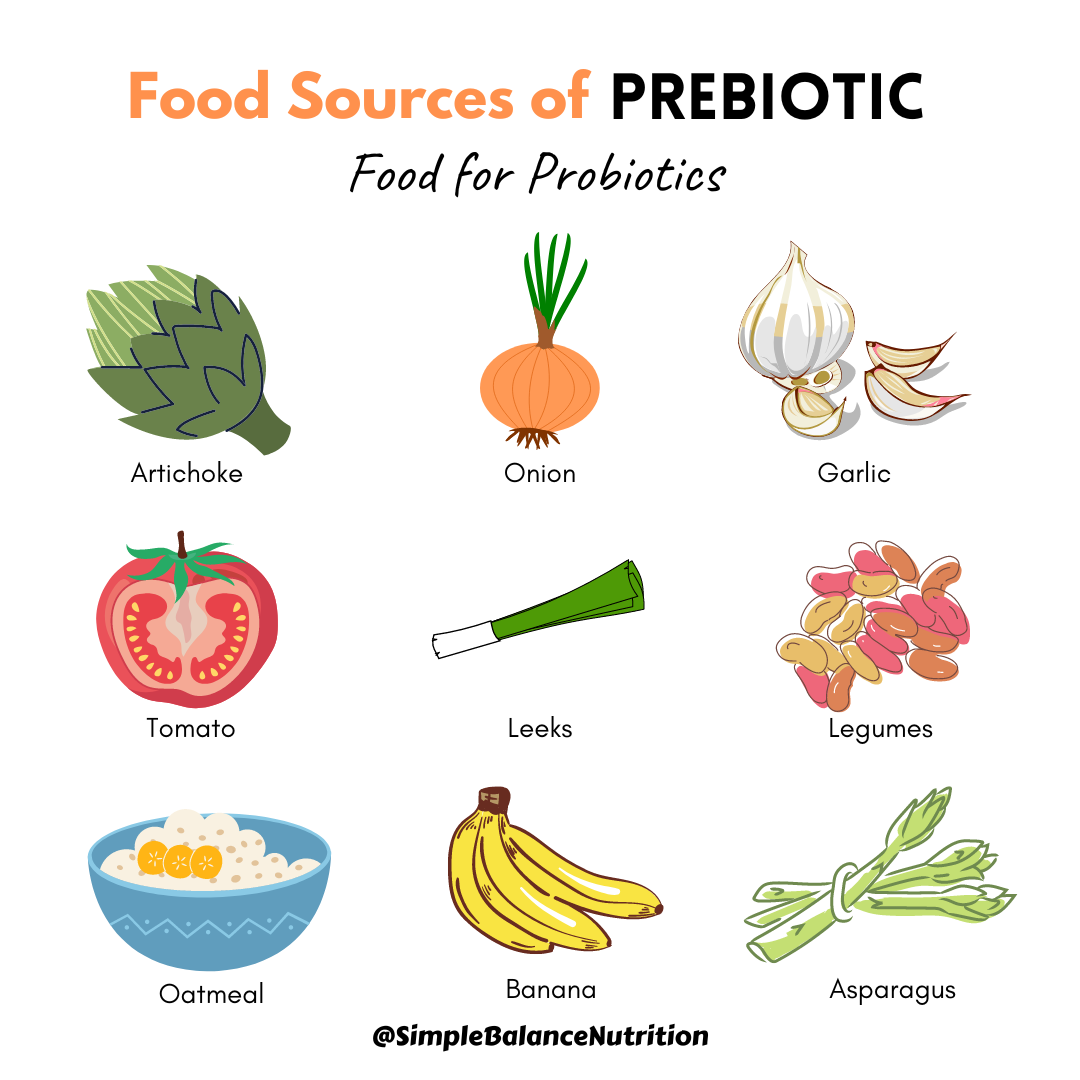
FOS, GOS and inulin are found naturally in these foods:
Vegetables
- Artichoke
- Asparagus
- Bananas
- Garlic
- Leeks
- Onion
- Tomatoes
Grains
- Barley
- Rye
- Whole Grains
Roots
- Chicory Root (菊苣根)
- Dandelion Root (蒲公英根)
- Elecampane Root (土木香根)
Galacto-Oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Fermented dairy products like yogurt, buttermilk and kefir
- Breast milk (Hooray!!!) – breastfed babies suffer fewer infections than formula-fed babies
HEALTH BENEFITS OF PREBIOTICS
Prebiotics act as “food” for probiotics which help to keep a healthy balance of bacteria in the digestive system. Eating prebiotic-containing foods often contain fibre and other nutrients. It also enhances calcium absorption. More research is still needed to find out if prebiotics are linked to other specific health benefits. However, if you do not consume foods that are naturally rich in prebiotics, you can still have a healthy gut by following a healthy and balanced diet
WHERE CAN YOU FIND PROBIOTICS
Probiotics are healthy bacteria that are either in supplements form or added into certain foods like yogurt, cheese, milk, juice, and cereal. The most common probiotic bacteria added to foods are Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species. It is better to read the ingredient list and make sure the product contains the right bacteria. To understand the strains of probiotics, read here.

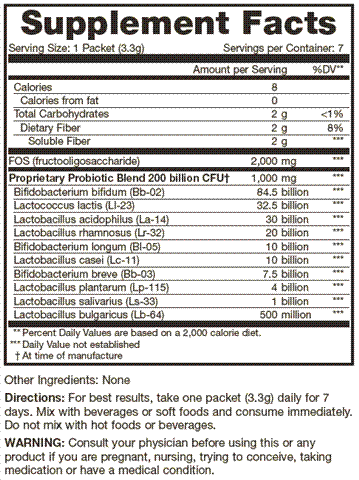
NAME TO LOOK FOR
Look at the Nutrition Facts or ingredient lists or products packaging for the names:
HEALTH BENEFITS OF PROBIOTICS
There are many potential health benefits of adding probiotics to your children’s diet.
- Decreasing the severity and duration of diarrhea cause by gastroenteritis – Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
- Preventing antibiotic-induced diarrhea – Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium lactis Bb1
- Reducing abdominal pain in children with IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) – Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
- Reducing eczema severity – Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Reducing symptoms of colic in babies – Lactobacillus reuteri
- Boosting immunity, especially with upper respiratory tract infections – Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium lactis Bb-12
- It is unclear if prebiotics or probiotics offer any long-term protection against allergies
It is not yet clear how much probiotics will give you health benefits. However, it is recommended that regular, long-term use is needed to keep healthy bacteria in your digestive system. Please noted that the positive effects of probiotics vary from person to person and strain(s). Individuals who do not consume foods with probiotics can still have a healthy digestive system by eating a healthy diet.
SAFETY CONCERNS
There are many brands and strains of probiotics that can be found at the pharmacy these day which can leave parents confused. Like many other supplements, over-the-counter prebiotics & probiotics are poorly regulated. That means that there are no rules for how much prebiotics/probiotics there should be in a food or how to label them on food packaging. If you decide to take a supplement, please check to make sure it has NPN, DIN or a DIN-HM number (somewhere on the bottle). Remember, being regulated does not guarantee that probiotics are effective. It only means that the product contains what is stated on the label and that they are safe to take.
It is recommended to choose the probiotic supplement is meant specifically for children – chewable or in a drink form, and it should be refrigerated. Remember to read the instructions regarding how much to give your children and pay attention to the expiry date.
BOTTOM LINE
Probiotics for your baby or child are a must if they have been on antibiotics. If you have a colicky baby or have troubles with constipation or eczema, I would try probiotic supplement. I would also recommend probiotic supplement for formula-fed babies or those born by C-section (who aren’t exposed to natural vaginal bacteria).
Did you know that I offer personalized one-on-one nutrition counselling for children and families? If this is something you’s like to learn more about, check out my service.


Leave A Comment