A healthy, well-balanced diet is important during pregnancy. Most fresh foods are completely safe for pregnant women, however, some foods should be avoided during pregnancy or if you’re trying to conceive, because most pregnancies are unplanned.
I’ve compiled a list of foods to avoid during pregnancy to serve as a quick guide.
WHY WE SHOULD AVOID THESE FOODS DURING PREGNANCY?
Food may carry germs that can make you sick. During pregnancy, your ability to fight off infections is decreased. Food poisoning (Food-Borne Illness) can also affect your unborn baby, such as listeriosis (李斯特菌病), salmonellosis (沙门氏菌病), toxoplasmosis (弓形虫病), and campylobacteriosis (弯曲杆菌病). Handling, preparing and storing food properly can reduce the chance of getting sick from food poisoning.
Pregnant women are 10 times more likely than other people to get a Listeria infection. Listeria infection can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, and preterm labor (here).
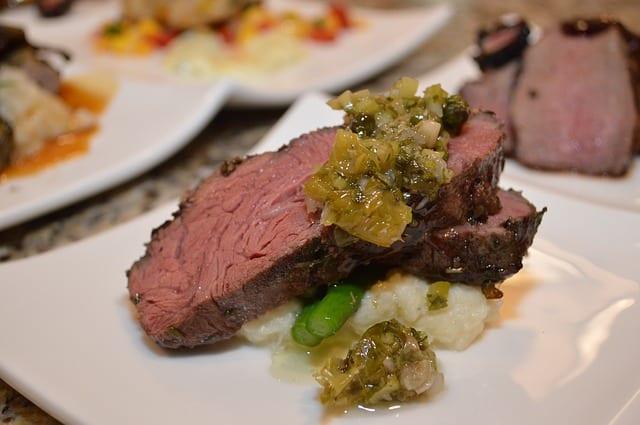

Raw or Undercooked Meat
All meat needs to be thoroughly cooked during pregnancy because of the risk of infection from several bacteria or parasites, including, Salmonella (沙门氏菌), E.Coli (大肠杆菌), Listeria (李斯特菌) and Toxoplasma (弓形虫).
Cook meat, poultry and fish to a safe internal temperature and avoid contamination from cutting boards and cooking utensils.
- Ground beef: 71°C (160°F )
- Poultry: 74°C (165°F)
- Fish: 70°C (158°F)
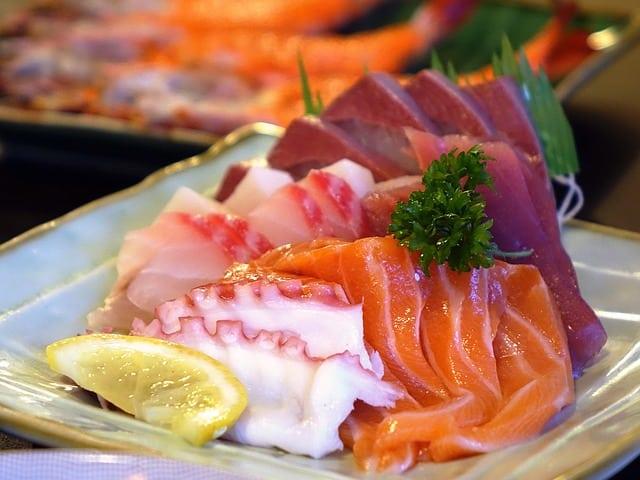

Raw or Undercooked Seafood and Shellfish
Raw or undercooked fish (including sushi, sashimi), especially raw shellfish (oysters, mussels and clams), should be avoided during pregnancy because of potentially harmful bacteria (Listeria) and parasites.
Smoked seafood is safe only when it is canned, shelf-stable, or cooked in a dish, such as casserole heated to 74°C (165°F).
Cooked sushi is safe to enjoy.
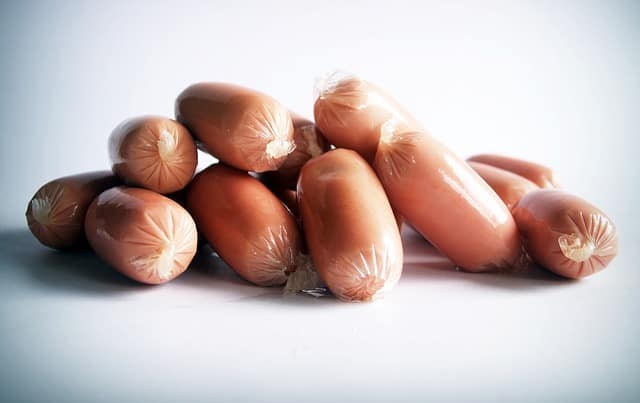

Deli Meats and Hotdogs
It’s advised to avoid deli meats and hotdogs if possible due to potential Listeria contamination. This bacteria can be killed through heat, so if you still want to eat deli meats during pregnancy, heat them until they are steaming hot, at least 74°C (165°F).
Hotdogs should also be heated until the middle is steaming hot.
Another concern is that deli meats and hotdogs often contain nitrites, and the effects of these ingredients on a developing fetus are still not fully understood.
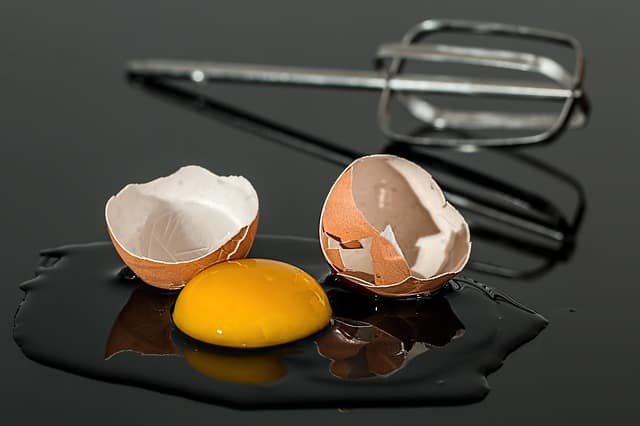

Raw or Undercooked Eggs
Eating raw or undercooked eggs can put pregnant women at an increased risk of Salmonella poisoning. Always cook eggs until both the yolk and white are firm. Certain foods may contain raw eggs, such as homemade Caesar salad dressing, hollandaise sauce, mayonnaise, unpasteurized eggnog, Tiramisu, custards and ice cream .
Use pasteurized egg products when recipes call for raw eggs.

Unpasteurized Dairy Products and Juices
Raw (unpasteurized) milk is milk from any animal (goat, cow, etc) and has not been pasteurized to kill harmful bacteria. Raw milk can contain bacteria such as Campylobacter, E.coli, Listeria, Salmonella, or Toxoplasma. To avoid getting these food borne illnesses, only consume pasteurized milk.
Avoid unpasteurized soft and semi-soft cheese, especially blue-veined varieties such as Feta, Brie, Camembert, havarti, Queso blanco, Queso fresco and Panela unless clearly labeled as pasteurized. These cheese made with unpasteurized milk may contain Campylobacter and Listeria. It is important to read labels carefully, to make sure that the milk being used in these products has been pasteurized. Instead, choose safe options such as hard cheese – Parmesan, cheddar or Swiss.
Homemade ice cream made with raw egg-based custard should be avoided unless pasteurized eggs are used. Commercially manufactured ice cream is safe.
Avoid unpasteurized juices, such as some fresh-pressed or cold-pressed juices. Home-squeezed juice is safe if fruits and vegetables are thoroughly washed. Smoothie are an even better choice during pregnancy, as they provide both nutrients and fiber.
If the cheese is coming in from another country, it may not be pasteurized.
High Mercury Fish
Fish is an excellent source of protein and healthy fats that support your baby’s brain and eye development. Pregnant women should eat at least 2 servings of fish per week.
However, some fish contain high levels of mercury, which is toxic to a developing fetus and can remain in the bloodstream for over a year.
Check out FDA Chart
High Mercury Fish:
- swordfish (旗鱼)
- tilefish (方头鱼)
- king mackerel (鲭鱼)
- shark (鲨鱼)
- marlin (马林鱼)
- orange roughy
- canned white tuna (Albacore) (大眼金枪鱼)
Low Mercury Fish:
- salmon (三文鱼)
- trout
- herring (鲱鱼)
- sardines (沙丁鱼)
- pollock (Boston bluefish)
- sole (鳎目鱼)
- flounder
- anchovy (凤尾鱼)
- char
- hake
- mullet
- smelt
- Atlantic mackerel (大西洋马鲛鱼)
- cod
- catfish
- tuna (light canned)/skipjack tuna (罐装金枪鱼)
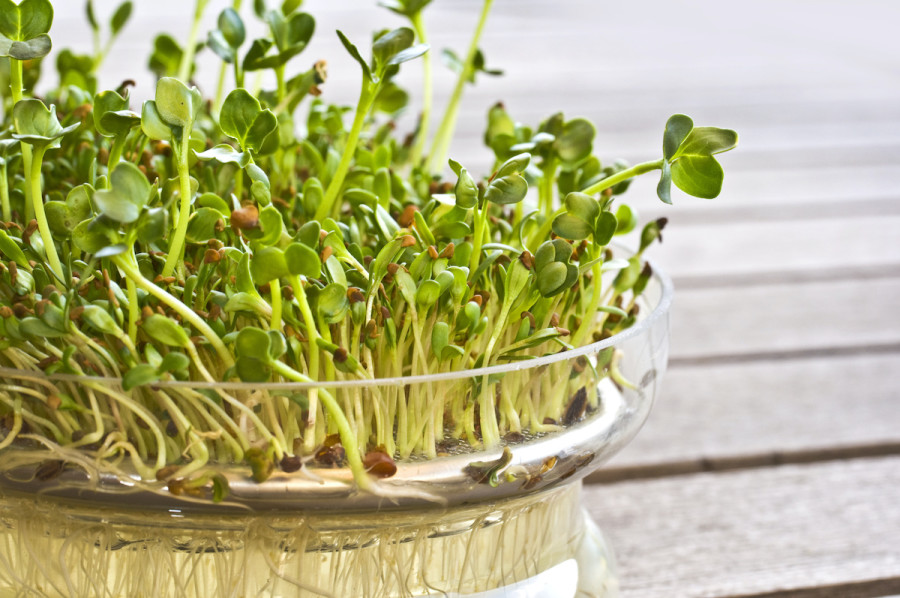
Raw Sprouts
Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish or mung bean sprouts, may be contaminated with Salmonella or E.coli. According to FDA, cook sprouts thoroughly can kill harmful bacteria and reduce the risk of illness.

Unwashed Vegetables and Fruit
It’s important to make sure that your vegetables are thoroughly washed to avoid any risk of Toxoplasmosis, because the soil in which vegetables are grown may be contaminated with E.coli or Salmonella.
Pregnant women should aim for 4-5 servings of vegetables and 2-3 servings of fruit daily. Keep cut vegetables and fruit in the fridge.
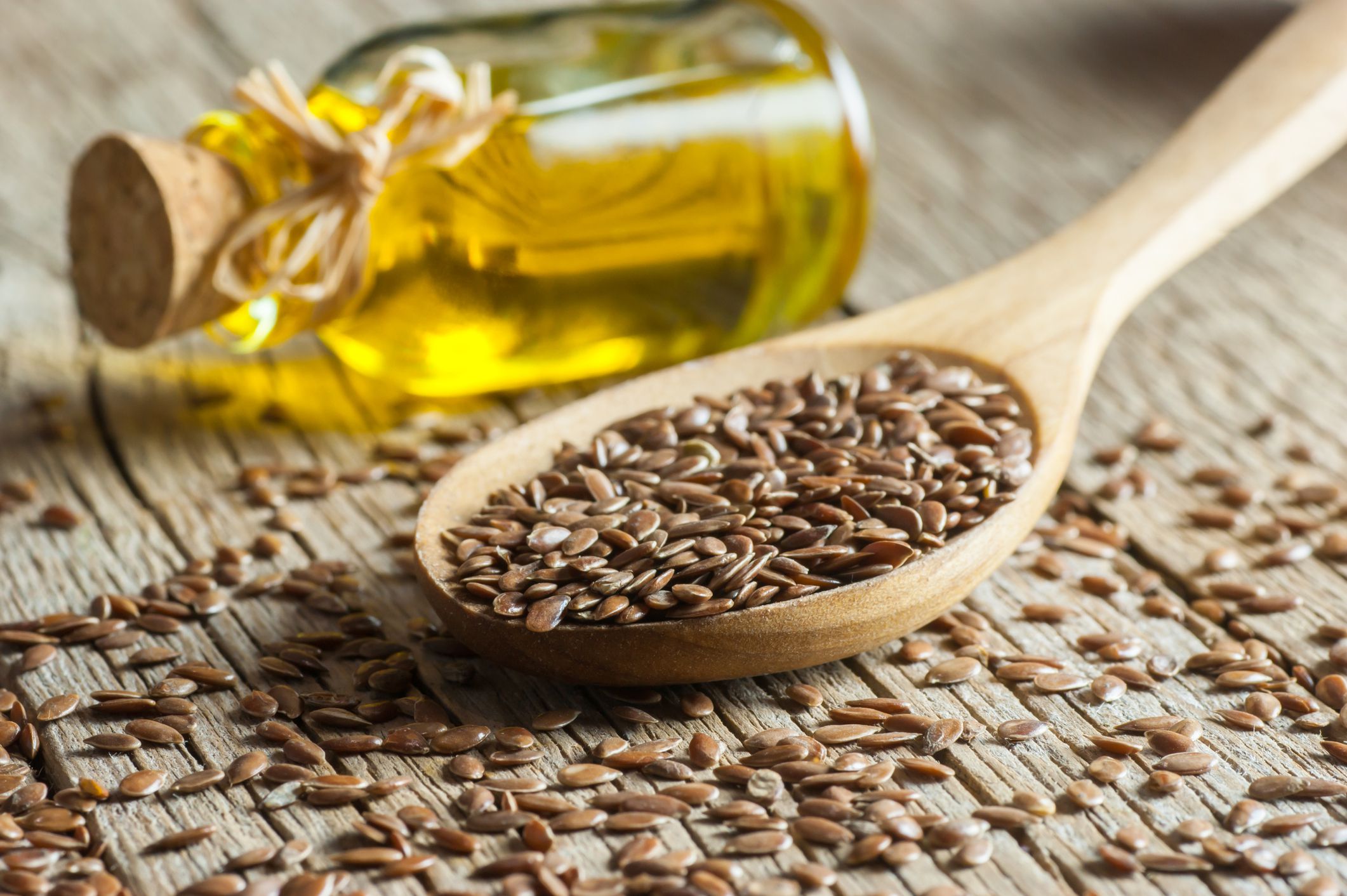
Flax Seeds and Flaxseed Oil
Flax seed may have mild extrogenic effects, and flaxseed oil has been linked to a higher risk of preterm birth. Because evidence is limited, avoid consuming large quantities of flaxseed oil during pregnancy, however, it is still safe to consume moderate amounts flax seeds commonly found in foods, such as flax seed bread.
Artificial Sweeteners
Moderate use of artificial sweeteners during pregnancy is considered safe. However, avoid Saccharin (Hermesetas®) and Cylamate (Sugar Twin®, Sweet N’Low®) as they are not recommended during pregnancy (here). Limit sweeteners in general, as they may replace more nutrient-dense foods.

Liver
Liver is high in iron but also contains very high levels of Vitamin A. Too much vitamin A can harm your baby (here).
Limit liver to 75g (2.5 oz) every two weeks.

Alcohol
Drinking alcohol can be harmful to the baby. No one knows what level of alcohol is safe for an unborn baby.
While you’re pregnant, or thinking about becoming pregnant, it’s safest not to drink any alcohol.
Alcohol passes directly from mother to baby through the placenta, baby’s liver can’t process it. Drinking increases the risk of miscarriage, preterm labor, low birth weight, and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) that can lead to growth problems, development delays, learning disabilities, and deformed facial features.
Alcohol used in cooking, such as Chinese rice wine, is usually safe is the dish has simmered or baked for at least one hour.

Caffeine
Caffeine has been associated with miscarriage, especially during the first trimester. However, small amounts of caffeine during pregnancy are fine for most people.
Limit your caffeine intake to about 300 mg per day or less (no more than 500 mL or 2 cups).
High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been shown to increase the risk of low birth weight and impaired fetal growth.
Caffeine is also found in tea (green and black teas contain about 30-50 mg per 250 mL or 1 cup), cola (23-40 mg per 250 mL or 1 cup), and chocolate (3-50 mg per 1 bar).

Herbal Teas
You may be thinking you should switch to herbal tea if you’re trying to cut back on caffeine, but that may not necessarily be your best pregnancy drink. Herbal teas can be made with fresh or dried flowers, leaves, seeds and/or roots.
Even though tea is all “natural”, the research on herbal tea is sparse and in some cases, there is concern that if consumed in excess, it could be problematic for a wide range of reasons. Some herbal products may stimulate uterine contractions, or increase the risk of birth defects. Again, it’s likely just a concern if you’re drinking large amounts daily, but always speak to your doctor first before making anything a regular part of your routine. (here, here).

BOTTOM LINE
Food intake during pregnancy is not about perfection, but about balance. While there are some foods you should avoid or limit to protect yourself and your baby from harmful bacteria, toxins, or excess nutrients, the most important thing is to focus on a safe, nourishing diet that supports a healthy pregnancy. When in doubt, choose cooked over raw, pasteurized over unpasteurized, and moderation over excess. And remember a well-balanced prenatal diet rich in whole foods will always do more for you and your growing baby than stressing over a long “do not eat” list.
Did you know that I provide one-on-one nutrition counselling services? If this is something you’d like to learn more about, check out my service.
Update: August 25, 2025




